Understanding The Intricate Fabric Of Mesopotamia Social Structure
Mesopotamia, often dubbed the "cradle of civilization," was home to some of the earliest complex societies in history. The social structure of Mesopotamia was a finely woven tapestry that reflected the dynamics of power, class, and occupation. The interrelationships among various social strata not only dictated individual lives but also influenced the development of legal systems, economic practices, and cultural norms within these ancient societies. With its rich history, the analysis of Mesopotamia's social structure provides valuable insights into how these early communities functioned and evolved over time.
The intricate social hierarchy in Mesopotamia encompassed a range of classes, from the ruling elite to the laboring masses, each playing a significant role in the overall functioning of society. Understanding this structure reveals much about the values, beliefs, and daily life of the Mesopotamian people. As we delve deeper into the layers of this structure, we will explore various aspects, including governance, economy, and family roles that were integral to Mesopotamian life.
Through an examination of the Mesopotamia social structure, we can also appreciate the complexities of their social relations and the impact of various factors such as religion, warfare, and trade. This article will outline the key features of this social hierarchy, answering essential questions about its composition and functionality, while also highlighting its significance in shaping one of the world's earliest civilizations.
What Were the Major Social Classes in Mesopotamia?
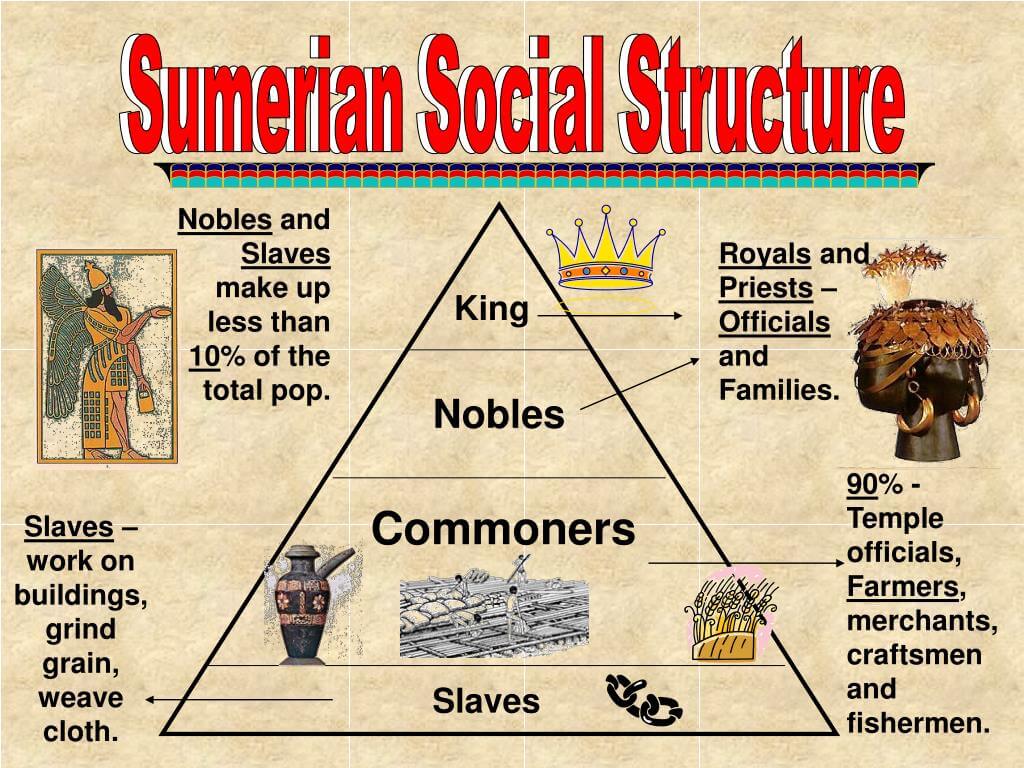
The social structure of Mesopotamia was divided into several key classes, each with distinct roles and responsibilities:
- Nobility: This upper class included kings, priests, and wealthy landowners who held significant power and influence.
- Commoners: Comprised of farmers, artisans, and merchants, the commoners formed the backbone of the economy.
- Slaves: Often prisoners of war or debtors, slaves occupied the lowest tier of the social hierarchy.
How Did Religion Influence the Mesopotamia Social Structure?
Religion played a crucial role in shaping the social structure of Mesopotamia. The priests were highly revered and often held more power than even the kings, as they were seen as intermediaries between the gods and the people. They managed temples, conducted rituals, and controlled vast land holdings. The intertwining of religion and governance solidified the social hierarchy, as moral and ethical standards were derived from religious beliefs.
What Role Did the Family Play in the Mesopotamian Society?
Family units in Mesopotamia were typically patriarchal, with the father serving as the head of the household. Family ties were crucial for social standing and inheritance. Women, while often relegated to domestic roles, had certain rights, such as owning property and conducting business. The family structure not only provided emotional support but also contributed to the economic stability of the household, reinforcing the importance of lineage and social status.
What Were the Occupations of Different Social Classes?
Occupations within the Mesopotamia social structure varied significantly across different classes:
- Nobility: Engaged in governance, military leadership, and religious activities.
- Commoners: Farmers, artisans, merchants, and laborers contributed to the economy through agriculture, craftsmanship, and trade.
- Slaves: Worked in households, farms, and temples, often performing manual labor.
How Did Trade Impact the Social Structure of Mesopotamia?
Trade played a vital role in shaping the Mesopotamia social structure, as it facilitated interactions between different cultures and regions. The wealth generated from trade allowed some commoners to rise in social status, challenging the rigid class structure. Merchants gained prominence and could accumulate wealth, leading to the emergence of a new social class that straddled the line between nobility and commoners. This evolving economic landscape highlighted the fluidity of social classes in Mesopotamia.
What Was the Role of Law in the Mesopotamia Social Structure?
The establishment of legal codes, such as the famous Code of Hammurabi, reinforced the social structure by outlining the rights and responsibilities of each class. Laws helped maintain order and defined the interactions between different social strata. Punishments were often class-specific, reflecting the hierarchical nature of Mesopotamian society and further entrenching social divisions.
How Did Warfare Influence the Social Hierarchy in Mesopotamia?
Warfare significantly affected the Mesopotamia social structure by altering power dynamics. Victorious leaders gained prestige and often ascended the social ladder, while the defeat of a city-state could lead to the enslavement of its citizens. The need for military service also created a class of warriors who could gain status through bravery and success in battles, thereby influencing the traditional social order.
In conclusion, the Mesopotamia social structure was a complex system that shaped the lives of its people and influenced the development of one of the earliest civilizations. By examining the various classes, their roles, and the factors that impacted this structure, we gain a deeper understanding of the social dynamics that characterized Mesopotamian life. The interplay of religion, family, occupation, trade, law, and warfare all contributed to the rich tapestry of this ancient society, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to resonate in modern times.
Drake's Playful Side: An Insight Into Drake Playing With Dick
Discovering 7movierulz: A Gateway To Free Movies And Entertainment
Unveiling The Allure: Sarah Hayes Topless